Watkins Glen International
| |
| Watkins Glen International | |
|---|---|
| Nicknames | The Glen |
| Capacity | 41,000 |
| Owner | International Speedway Corporation |
| Operator | International Speedway Corporation |
| Broke_ground | |
| Opened | 1953 |
| Closed | |
| Construction_cost | |
| Architect | |
| Former_names | |
| Events |
NASCAR Sprint Cup Series NASCAR Nationwide Series Grand-Am Rolex Sports Car Series IRL Firestone Indy Lights Sportscar Vintage Racing Association |
| Miles_first | True |
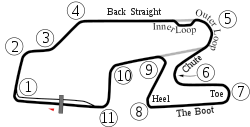
| Layout1 | Grand Prix Course |
| Surface | Asphalt/Concrete |
| Length km | 5.43 |
| Length mi | 3.40 |
| Turns | 11 |
| Banking | |
| Record time | 1:29.1919 |
| Record driver | Hélio Castroneves |
| Record team | Team Penske |
| Record year | 2007 |
| Record class | IRL IndyCar Series |
| Layout2 | 1971 Six Hours Course |
| Surface2 | Asphalt |
| Length km2 | 4.06 |
| Length mi2 | 2.454 |
| Turns2 | 8 |
| Banking2 | |
| Record time2 | 1:07.020 |
| Record driver2 | Jon Fogarty |
| Record team2 | GAINSCO/Bob Stallings Racing |
| Record year2 | 2007 |
| Record class2 | Grand-AmRolex Sports Car Series |
Watkins Glen International (nicknamed "The Glen") is an auto race track located near Watkins Glen, New York, at the southern tip of Seneca Lake. The facility is owned by International Speedway Corporation. It was long known around the world as the home of the United States Grand Prix, which it hosted for 20 consecutive years (1961–1980), but it has been home to road racing of nearly every class for over 50 years, including:
- Sports Car Club of America (SCCA) SPEED World Challenge
- Spec Miata
- NASCAR Nationwide Series
- NASCAR Sprint Cup Series
- NASCAR Whelen Modified Tour
- Formula Libre
- Formula One
- Can-Am
- Trans-Am
- Formula 5000
- International Race of Champions (IROC)
- Champ Car
- World Sportscar Championship
- Indy Racing League
Beginnings
The first races in Watkins Glen were initiated by Cameron Argetsinger, whose family had a summer home in the area. With Chamber of Commerce approval and SCCA sanction, the first Watkins Glen Grand Prix took place in 1948 on a 6.6mi course over the local roads. For the first few years, the races passed through the heart of the town with spectators lining the sidewalks, but after a car left the road in the 1952 race, killing one spectator and injuring several others, the race was moved to a new location on a wooded hilltop southwest of town. The original 6.6mi course is listed in the New York State and National Registers of Historic Places.
The new 4.6mi course for 1953 also used existing roads. The Watkins Glen Grand Prix Corporation was formed to manage spectators, parking and concessions. This arrangement lasted three years before a 2.35mi permanent race course was constructed on 550 acres (2.2 km²), overlapping part of the previous course. It was designed by Bill Milliken to be a smaller version of the original street circuit and laid out by several engineering professors from nearby Cornell University. Along with the annual SCCA race, the track hosted its first professional race (NASCAR Grand National Division) in 1957 and became truly international when the Formula Libre race attracted some of the best road racing drivers in the world, including Jack Brabham, Stirling Moss, Phil Hill and Dan Gurney from 1958 through 1960.
Home of the United States Grand Prix

After two less-than-successful US Formula One events in 1959 (Sebring, Florida) and 1960 (Riverside, California), promoters were looking for a new venue for an American Grand Prix in 1961. Just six weeks before the scheduled date for another Formula Libre race that fall, Argetsinger was tapped to get Watkins Glen ready to host the final round of the Formula One World Championship instead. While many of the necessary preparations had already been made for the Formula Libre race, new pits were constructed for the F1 Grand Prix according to the European style of pit boxes with overhead cover. Seven American drivers participated, and the race was won by British driver Innes Ireland with American Dan Gurney second. The sole disappointment of the weekend was that newly-crowned American World Champion Phil Hill appeared only as the event's Grand Marshal, not on track in his shark-nosed Ferrari, as the team was still mourning the death of Count Wolfgang von Trips at Monza the previous race.
The United States Grand Prix at The Glen quickly became a fall tradition as huge crowds of knowledgeable racing fans flocked to upstate New York each year amid the spectacular fall colors. The race was also among the most popular on the global Grand Prix calendar with the teams and drivers because its starting and prize money often exceeded those of the other races combined. The race received the Grand Prix Drivers' Association award for the best organized and best staged GP of the season in 1965, 1970 and 1972.
One fixture of the USGP at The Glen was the starter for the races, "Tex" Hopkins. Wearing a lavender suit, clenching a big cigar in his mouth, and giving the job everything he had, Hopkins was the most recognizable starter in Grand Prix racing. Once the cars had taken their places, Hopkins strode across the front of the grid with his back to the field, turned, and jumped into the air, waving the green flag to start the race. At the finish, he would meet the winner in similar fashion, this time waving the checkered flag as the car crossed the line.
Before the 1971 race, the course underwent its most significant changes of the Grand Prix era, as it was extended from 2.35mi to 3.377mi by the addition of four corners in a new section called the 'Boot' or 'Anvil'. The new layout departed from the old course near the south end into a curling downhill left-hand turn through the woods. The track followed the edge of the hillside to two consecutive right-handers, over an exciting blind crest to a left-hander and back onto the old track. In addition, the circuit was widened and resurfaced, and both the pits and start/finish line were moved back before the northwest right-angle corner known as "The 90."
Despite the improvements, the circuit became unable to safely handle the increasingly faster and stiffer ground effect cars of the late 70s and a few horrendous, sometimes fatal accidents and increasingly rowdy segments of the crowd began to tarnish its image. Finally, in May, 1981, several months after Alan Jones had won the 1980 race for Williams, the International Auto Sports Federation removed the race from its schedule because the track had failed to pay its $800,000 debt to the teams.
American road-racing Mecca
The Glen hosted a variety of other events throughout the Grand Prix years: from Can-Am, Trans-Am, IROC and Endurance Sports car racing to Formula 5000 and the CART series, these races strengthened the circuit's reputation as the premier road racing facility in the United States. From 1968 through 1981, the "Six Hours at The Glen" endurance race featured top drivers like Mario Andretti, Jacky Ickx, Pedro Rodríguez and Derek Bell. Different races were sometimes featured together on the same weekend (e.g., Six Hours and Can-Am) and drew sizable crowds, but without a Formula One race, the circuit struggled to survive. It finally declared bankruptcy and closed in 1981.
Reincarnation
For two years, the track was not well maintained and hosted only a few SCCA meets without spectators. In 1983, Corning Enterprises, a subsidiary of nearby Corning, partnered with International Speedway Corporation to purchase the track and rename it Watkins Glen International.
The renovated track, with the chicane at the bottom of the Esses removed, reopened in 1984 with the return of IMSA with the Camel Continental I, which would be conducted until 1995, with the last two years under the name "The Glen Continental" after Camel's withdrawal from IMSA. (The event was numbered with Roman numerals.)
In 1986, the top NASCAR series returned to Watkins Glen after a long layoff, holding one of only three road races on its schedule (two beginning in 1988), using the 1971 Six Hours course, raced when the new section off the Loop-Chute was not finished in time. As the cars come off the Loop-Chute, instead of making the downhill left into Turn 6, the cars shot straight through the straight and headed towards Turn 10, as was the case from 1961 until 1970.
NASCAR Busch Series (Now Called Nationwide Series) action would arrive in 1991 with a 150mi} race on the weekend of the Camel Continental, won by Terry Labonte, who would be a master of the circuit during its Busch Series races, winning the inaugural race, and winning three consecutive races from 1995 until 1997. The 1995 race would be the first conducted as a 200mi race, and became the first Busch Series race to be televised on broadcast network television, as CBS broadcast the race live until TNN took over in 1997.
Only twice—1998 and 1999—did a Busch Series regular driver win the race. The first seven races were won by Winston Cup Series (Now Sprint Cup Series) regular drivers, sometimes referred as "Buschwhackers," during their off-week. In 1998, the race went against the Cup race in Sonoma, California, eliminating the idea, and stayed that way until 2000. In 2001, the race was run the day after the first Saturday in July.
However, the race was eliminated from the schedule after the 2001 season, only to return in 2005 as an undercard to the Nextel Cup (now Sprint Cup Series) race.
A pair of incidents took place in 1991 resulted in a massive overhaul of the circuit's safety. During the IMSA Camel Continental VIII, Tommy Kendall's prototype crashed in Turn 5, severely injuring his legs. Seven weeks later, NASCAR driver J. D. McDuffie died in an accident at the same site. Track officials added a bus stop chicane to the back straight in 1992 .
In 1996, the Glen Continental reverted back to a six hour format, and was once again called the Six Hours At The Glen with the IMSA format, and stayed there until a split in sports car racing in the United States. In 1998, the race became an event sanctioned by the Sports Car Club of America under their United States Road Racing Championship. In 1999, the FIA GT series staged a 500 km race after the USRRC canceled the rest of their season before their event at the track. The following year, the 6 hour race returned once again with the newly-founded Grand American Road Racing Association (Grand-Am) sanctioning the event.
In 1997, International Speedway Corporation became the sole owner of the historic road course, as Corning Enterprises believed they had completed their intended goals to rebuild the race track and increase tourism in the southern Finger Lakes region of New York State.
The circuit annually hosts one of the nation's premier vintage events, the Zippo U.S. Vintage Grand Prix. When the 50th anniversary of road racing in Watkins Glen was celebrated during the 1998 racing season, this event was the climax, returning many original cars and drivers to the original Template:Convert/miTemplate:Convert/test/A street circuit through the village during the Grand Prix Festival Race Reenactment.
After a 25 year layoff, major-league open wheel racing returned to the track as one of three road courses on the 2005 Indy Racing League schedule. In preparation, the circuit was overhauled again. Grandstands from Pennsylvania's Nazareth Speedway, which had closed, were installed, the gravel in The 90 was removed and replaced with a paved runoff area, and curbing was cut down for the Indy Racing League event. Previously, the high curbing in the chicane had become a place where NASCAR Sprint Cup Series cars would bounce high off the curbing, creating an ideal opportunity for cars to lose control, and to slow cars. Other areas of the track received improvements as well: the exits of turn 2 (the bottom of the esses), the chicane, turn 6 (the entrance to the boot), turn 9 and turn 11 all had additional runoff areas created and safety barrier upgrades. The carousel run off has been paved, as well as turn 1 (the 90) and the esses are being paved in the winter of 06-07. Augmenting what was already in place along the front stretch, additional high safety fences were installed on the overpasses crossing the service roads at the top of the esses and just out of the boot immediately after the exit of turn 9.
Another overhaul for 2006 made fundamental changes to the circuit for the first time since 1992. Officials installed a new control tower, which includes booths for the officials, timing and scoring, television and radio (the new position allows broadcasters to see more action from Turn 10 through the foot of the Esses), and the public address announcer on top of the new frontstretch grandstand, moving the start-finish line further ahead of the Sprint bridge, as the start-finish line is moved Template:Convert/ftTemplate:Convert/test/A further towards The 90 in order to accommodate the new timing and scoring post. The new start-finish line also means the starting lights used for club races is moved further ahead, creating more action off Turn 11 as tactics will change with the later finish line, where slingshot moves could become paramount to the finish. Other changes to the infrastructure include the purchase of adjoining property. Most of Bronson Hill Road is now incorporated as a service road to the facility. A new section of Bronson Hill leading up from NY 414 has been built as the main ingress road to the facility, bending south at Gate 6 and continuing to County Road 16, just south of the credentials and sheriff's office buildings.
Track safety is also always changing and constant training is needed. Race Services Inc. provides the track with volunteers to work Fire-Rescue, Medical, Grid personnel and Corner workers to help keep both the drivers and spectators safe.
Cameron Argetsinger remains as an advisor to the circuit, and the track named the trophy for the inaugural Watkins Glen Indy Grand Prix presented by Argent in his honour.
On March 6, 2007 just before 9pm, fire destroyed the recently remodeled Glen Club situated on top of the esses. Originally called the Onyx Club (named for the sponsor, Onyx Cologne), the Glen Club was used primarily as an upscale venue for race fans. After being recently remodeled, it was being advertised as a social venue for locals to use for weddings, business meetings, etc. No cause could be determined and the building was a total loss. The loss included irreplaceable, unique original motorsports artwork donated to the facility by several artists along with other racing memorabilia. Glen officials were quoted in local media stories as being adamant that the loss of the Glen Club would in no way affect the 2007 racing schedule.
For 2007, Watkins Glen International again made improvements to the facility, specifically the track surface. All of turns 1 (the "90"), 5 (the "Loop-Chute") and 6 (entry turn into the "Boot") have been repaved. A temporary "Glen Club" replaced the permanent structure destroyed by fire at the races in 2007 with plans in the works to replace it with another permanent building. New sponsors for both the INDY and NASCAR weekends were signed to multi-year deals. Camping World is now the sponsor of the "Camping World Grand Prix" INDY weekend at the Glen through 2010. NASCAR weekend at the Glen received a double shot--Zippo Manufacturing announced a three year extension of the Busch/Nationwide Series race, the "Zippo 200". The Sprint Cup series is now known as "The Centurion Boats at the Glen", another multi-year deal that goes through 2009. Additionally, Brad Penn lubricants of Pennsylvania (former Kendall Oil refinery) has been announced as the sponsor of the annual vintage sports car weekend for 2007 and 2008.
A new media centre is being constructed to replace the former building, which had also been the control tower with the 1971 improvements. The aging structure had been the bane of many professional media members in recent years with many uncomplimentary things published and broadcast about its inadequacies, especially the lack of insulation, air conditioning, few (if any) amenities that other facilities have, which resulted in race control moving to the new control tower at the start-finish line in 2006. The new media centre will be moved back in order to allow a full 43-car NASCAR grid.
Records
- FIA Formula One Qualifying (GP Course): Bruno Giacomelli, 93.291 sec. (130.315 mph/209.722 km/h), 1980
- FIA Formula One Race (199.24mi/318.784 km): Alan Jones, 1 hr 34 min 36 sec (126.367 mph/203.368 km/h), 1980
- FIA Formula One Qualifying (2.35mi course): Jacky Ickx, 63.07 (134.136 mph/214.617 km/h), 1970
- FIA Formula One Race (253.8mi/408.2 km): Emerson Fittipaldi 1 hr 57 min 33.2sec (129.541 mph/207.265 km/h), 1970
- NASCAR Sprint Cup Series Qualifying: Jeff Gordon, 70.798 sec. (124.580 mph/199.323 km/h), 2003
- NASCAR Sprint Cup Series Race (220.5 miles): Mark Martin, 2 hrs 26 min 17 sec (100.300 mph/160.48 km/h), 1995
- NASCAR Nationwide Series Qualifying: Kurt Busch, 71.861 sec. (121.052 mph/193.683 km/h), 2007
- NASCAR Nationwide Series Race (200.9 miles): Terry Labonte, 2 hrs 11 min 47 sec.(91.468 mph/146.348 km/h), 1996
- IRL IndyCar Series Qualifying: Hélio Castroneves, 89.1919 sec. (136.021 mph/218.905 km/h), 2007
- Grand Am Rolex Sports Car Series (NASCAR Course) Qualifying: Jon Fogarty, 67.020 sec. (131.603 mph/211.794 km/h), 2007
See also
- List of Formula One circuits
- List of Champ Car circuits
- List of NASCAR race tracks
- Summer Jam at Watkins Glen, a 1973 rock festival held at the raceway that attracted 600,000 people.
References
- Watkins Glen International
- Short History of Road Racing at Watkins Glen
- GP Encyclopedia, Circuits: Watkins Glen
- "Watkins Glen Loses Race; Track Failed to Pay Debts.", New York Times, 8 May, 1981.
External links
- Trackpedia guide to driving this track
- Aerial Photo
- Watkins Glen International Page on NASCAR.com
- Watkins Glen Grand Prix Fest
- Indy Racing League 2006 Video Footage
- Race Services Inc. website
- Track history and other info
| Grand-Am circuits | |
|---|---|
|
Daytona •
Hermanos Rodríguez •
Homestead •
Virginia •
Laguna Seca •
Lime Rock •
Watkins Glen •
Mid-Ohio •
Barber •
Montréal •
Infineon •
Miller
|
| Tracks of the Indy Racing League | |
|---|---|
|
Indianapolis Motor Speedway · Chicagoland · Homestead · Iowa · Kansas · Kentucky · Milwaukee · Motegi · Nashville · Richmond · Texas
|
| Ovals | Atlanta · California · Chicago · Gateway · Homestead · Indianapolis · Las Vegas · Loudon · Michigan · Milwaukee · Nazareth · Ontario · Phoenix · Pocono · Sanair · Texas · Texas World · Trenton | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Road courses | Cleveland · Edmonton · Laguna Seca · Mid-Ohio · Montreal · Mont-Tremblant · Portland · Riverside · Road America · Watkins Glen | |||
| Street circuits | Belle Isle · Caesars Palace · Denver · Detroit ·
Houston · Las Vegas · Long Beach · Meadowlands · Miami · Reliant Park · San Jose · St. Pete · Tamiami Park · Toronto · Vancouver | |||
| International | Assen · Brands Hatch · EuroSpeedway · Mexico City · Monterrey · Motegi · Rio · Rockingham · Surfers Paradise · Zhuhai · Zolder | |||
