Difference between revisions of "Basilicata"
m |
|||
| (18 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{X}} | ||
{{Infobox_RegionIT | | {{Infobox_RegionIT | | ||
name = Basilicata | | name = Basilicata | | ||
| Line 4: | Line 5: | ||
isocode = | | isocode = | | ||
capital = [[Potenza]] | | capital = [[Potenza]] | | ||
| − | governor = Vito De Filippo<br />(''[[The Union (political coalition)| | + | governor = Vito De Filippo<br />(''[[Democracy is Freedom - Daisy|DL]]''-''[[The Union (political coalition)|Union]]'') | |
zone = [[South Italy]] | | zone = [[South Italy]] | | ||
province = [[Province of Matera|Matera]]<br />[[Province of Potenza|Potenza]] | | province = [[Province of Matera|Matera]]<br />[[Province of Potenza|Potenza]] | | ||
| Line 11: | Line 12: | ||
area = 9,995 | | area = 9,995 | | ||
areapercent = 3.3 | | areapercent = 3.3 | | ||
| − | population_as_of = | + | population_as_of = 2006 est. | |
populationrank = 18 th | | populationrank = 18 th | | ||
| − | population = | + | population = 594,086 | |
populationpercent = 1.0 | | populationpercent = 1.0 | | ||
| − | populationdensity = | + | populationdensity = 59 | |
| − | coatofarms = [[Image:Basilicata-Bandiera.png]] | | + | coatofarms = [[Image:Basilicata-Bandiera.png|220px]] | |
map = [[Image:Italy Regions Basilicata 220px.png]] | | map = [[Image:Italy Regions Basilicata 220px.png]] | | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | '''Basilicata''' is a region in the south of [[Italy]], bordering on [[Campania]] to the west, [[Puglia]] to the east, [[Calabria]] to the south, it has one short coastline on the [[Tyrrhenian Sea]] and another of the [[Gulf of Taranto]] in the [[Ionian Sea]] to the south-east. The region covers 9,992 [[square kilometre| | + | |
| + | '''Basilicata''' is a region in the south of [[Italy]], bordering on [[Campania]] to the west, [[Puglia]] to the east, [[Calabria]] to the south, it has one short coastline on the [[Tyrrhenian Sea]] and another of the [[Gulf of Taranto]] in the [[Ionian Sea]] to the south-east. The region covers 9,992 [[square kilometre|km²]] and in [[2001]] had a population of 597,768 (pop. density 60) | ||
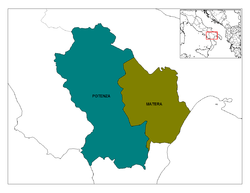
The regional capital is [[Potenza]]. The region is divided into two provinces: [[Province of Potenza|Potenza]] and [[Province of Matera|Matera]]. | The regional capital is [[Potenza]]. The region is divided into two provinces: [[Province of Potenza|Potenza]] and [[Province of Matera|Matera]]. | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Basilicata Provinces.png|thumb|left|250px|Provinces of Basilicata]] | |
The region is as a whole mountainous, the highest point of the southern [[Apennines]] being [[Monte Pollino]] (7325 ft). [[Monte Vulture]], in the northwest corner ([[Vulture area]]), is an extinct volcano (4365 ft). The mountainous terrain made communications difficult until modern times, and Basilicata was one of the least developed provinces of Italy. | The region is as a whole mountainous, the highest point of the southern [[Apennines]] being [[Monte Pollino]] (7325 ft). [[Monte Vulture]], in the northwest corner ([[Vulture area]]), is an extinct volcano (4365 ft). The mountainous terrain made communications difficult until modern times, and Basilicata was one of the least developed provinces of Italy. | ||
| + | Basilicata also used to be one of the poorest regions in Italy, but has become significantly richer over the past couple of years because of the discovery of oil. | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
| − | In Roman times the district was called [[Lucania]] and was administered together with the district of [[Bruttium]] (inhabited by the [[Bruttii]]), to the south. The district of Lucania was so called from the people bearing the name ''Lucani'' (Lucanians), who invaded the country about the middle of the [[5th century BC]], driving the indigenous tribes, known to the Greeks as [[Oenotrians]], [[Chones]], and [[Leuterni]] (or Leutarni), into the mountainous interior. The coasts on both sides were occupied by powerful [[Greek colonies]], part of [[Magna Graecia]]. | + | In Roman times the district was called [[Lucania]] and was administered together with the district of [[Bruttium]] (inhabited by the [[Bruttii]]), to the south. The district of Lucania was so called from the people bearing the name ''[[Lucani]]'' (Lucanians), who invaded the country about the middle of the [[5th century BC]], driving the indigenous tribes, known to the Greeks as [[Oenotrians]], [[Chones]], and [[Leuterni]] (or Leutarni), into the mountainous interior. The coasts on both sides were occupied by powerful [[Greek colonies]], part of [[Magna Graecia]]. |
| − | The Lucanians | + | The Lucanians were engaged in hostilities with the Greek colony of [[Taranto|Taras/Tarentum]], and with [[Alexander of Epirus|Alexander, king of Epirus]], who was called in by the Tarentine people to their assistance, in [[326 BC]], thus providing a precedent for Epirote interference in the affairs of Magna Graecia. |
| − | + | In [[298 BC|298]], [[Livy]] records, they made alliance with Rome, and Roman influence was extended by the colonies of [[Venusia]] ([[291 BC|291]]), [[Paestum]] (Greek Posidonia, refounded in [[273 BC|273]]), and above all Roman Tarentum (refounded in [[272 BC|272]]). Subsequently, however, the Lucanians suffered by choosing the losing side in the various wars on the peninsula in which Rome took part. They were sometimes in alliance with Rome, but more frequently engaged in hostilities, during the [[Samnite wars]]. When [[Pyrrhus of Epirus]] landed in Italy, [[281 BC|281]] they were among the first to declare in his favor, and after his abrupt departure they were reduced to subjection, in a ten year campaign ([[272 BC|272]]). Enmity continued to run deep; they espoused the cause of Hannibal during the [[Second Punic War]] ([[216 BC|216]]), and Lucania was ravaged by both armies during several campaigns. The country never recovered from these disasters, and under the Roman government fell into decay, to which the [[Social War]], in which the Lucanians took part with the Samnites against Rome ([[90 BC|90]] - [[88 BC]]), gave the finishing stroke. In the time of Strabo the Greek cities on the coast had fallen into insignificance, and owing to the decrease of population and cultivation malaria began to obtain the upper hand. The few towns of the interior were of no importance. A large part of the province was given up to pasture, and the mountains were covered with forests, which abounded in wild boars, bears and wolves. | |
| − | + | ==See also== | |
| + | *[[Lucania]] | ||
| + | *[[Lucani]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| − | *[http://www.regione.basilicata.it/ Official Site] | + | * [http://www.regione.basilicata.it/ Official Site] |
| − | *[http://www.italy-weather-and-maps.com/maps/italy/basilicata.gif Map of Basilicata] | + | * [http://www.italy-weather-and-maps.com/maps/italy/basilicata.gif Map of Basilicata] |
| − | *[http://www.aptbasilicata.it/ Basilicata Tourist Office | + | * [http://www.aptbasilicata.it/ Basilicata Tourist Office] |
| − | + | * [http://www.italianvisits.com/basilicata/ ItalianVisits.com: Basilicata] | |
| − | *[http://www.italianvisits.com/basilicata/ ItalianVisits.com] | + | |
| − | {{Italy}} | + | {{Regions of Italy}} |
| + | {{Province of Matera}} | ||
| + | {{Province of Potenza}} | ||
[[Category:Basilicata|*]] | [[Category:Basilicata|*]] | ||
[[Category:NUTS 2 Statistical Regions of Europe]] | [[Category:NUTS 2 Statistical Regions of Europe]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Wine regions of Italy]] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:23, 1 August 2009
Basilicata is a region in the south of Italy, bordering on Campania to the west, Puglia to the east, Calabria to the south, it has one short coastline on the Tyrrhenian Sea and another of the Gulf of Taranto in the Ionian Sea to the south-east. The region covers 9,992 km² and in 2001 had a population of 597,768 (pop. density 60)
The regional capital is Potenza. The region is divided into two provinces: Potenza and Matera.
The region is as a whole mountainous, the highest point of the southern Apennines being Monte Pollino (7325 ft). Monte Vulture, in the northwest corner (Vulture area), is an extinct volcano (4365 ft). The mountainous terrain made communications difficult until modern times, and Basilicata was one of the least developed provinces of Italy. Basilicata also used to be one of the poorest regions in Italy, but has become significantly richer over the past couple of years because of the discovery of oil.
History
In Roman times the district was called Lucania and was administered together with the district of Bruttium (inhabited by the Bruttii), to the south. The district of Lucania was so called from the people bearing the name Lucani (Lucanians), who invaded the country about the middle of the 5th century BC, driving the indigenous tribes, known to the Greeks as Oenotrians, Chones, and Leuterni (or Leutarni), into the mountainous interior. The coasts on both sides were occupied by powerful Greek colonies, part of Magna Graecia.
The Lucanians were engaged in hostilities with the Greek colony of Taras/Tarentum, and with Alexander, king of Epirus, who was called in by the Tarentine people to their assistance, in 326 BC, thus providing a precedent for Epirote interference in the affairs of Magna Graecia.
In 298, Livy records, they made alliance with Rome, and Roman influence was extended by the colonies of Venusia (291), Paestum (Greek Posidonia, refounded in 273), and above all Roman Tarentum (refounded in 272). Subsequently, however, the Lucanians suffered by choosing the losing side in the various wars on the peninsula in which Rome took part. They were sometimes in alliance with Rome, but more frequently engaged in hostilities, during the Samnite wars. When Pyrrhus of Epirus landed in Italy, 281 they were among the first to declare in his favor, and after his abrupt departure they were reduced to subjection, in a ten year campaign (272). Enmity continued to run deep; they espoused the cause of Hannibal during the Second Punic War (216), and Lucania was ravaged by both armies during several campaigns. The country never recovered from these disasters, and under the Roman government fell into decay, to which the Social War, in which the Lucanians took part with the Samnites against Rome (90 - 88 BC), gave the finishing stroke. In the time of Strabo the Greek cities on the coast had fallen into insignificance, and owing to the decrease of population and cultivation malaria began to obtain the upper hand. The few towns of the interior were of no importance. A large part of the province was given up to pasture, and the mountains were covered with forests, which abounded in wild boars, bears and wolves.
See also
External links
| Regions of Italy | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abruzzo • Aosta Valley • Apulia • Basilicata • Calabria • Campania • Emilia-Romagna • Friuli-Venezia Giulia • Lazio • Liguria • Lombardy • Marche • Molise • Piedmont • Sardinia • Sicily • Trentino-South Tyrol • Tuscany • Umbria • Veneto | ||||